Tech Write For Us | Cyber Security, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Data Science, Internet Of Things, Big Data, Blockchain, Computer Science
Are you a tech enthusiast like us with a passion for writing and a desire to share your technology knowledge and insights with a wider audience? If so, we invite you to write for us and submit your articles for consideration on our blog.
Our blog covers a wide range of technology related topics including software/apps, latest technology updates, gadgets, artificial intelligence, SEO and product reviews. We are always on the lookout for new and original content from the technology world to engage our tech-savvy readers.
Technoiva: Technology Blog Write For Us
Each and every one of the bloggers and companies that choose to publish with us is greatly valued. We have a vast online community of tech-loving people that we can connect you with by sharing your content on our website and social media.
To submit an article to publish on our blog, email us at [email protected]. We’ll contact you within 48 hours. We’ll try to catch you ASAP.
Read The Following Instructions Before Writing To Our Tech Blog:
- Title for blog posts should be engaging and no more than 60 characters.
- The content must be unique, well-written, and easy to understand, We don’t allow duplicate or plagiarized content.
- Try for a word count of 900+, include headings, and check for grammar errors before sending us.
- Please provide an original featured image that is of good quality and the appropriate resolution.
- Affiliate and non-promotional links will be rejected.
- Share author name and short author bio.
Benefits Of Writing Article For Technoiva
- Increase your visibility and credibility
- Improve your search engine rankings and drive more traffic to your site
- New opportunities and collaborations
- Build your reputation and credibility
- Increase awareness of your brand
Semrush And Ahrefs Traffic Stats
Semrush Traffic Stats
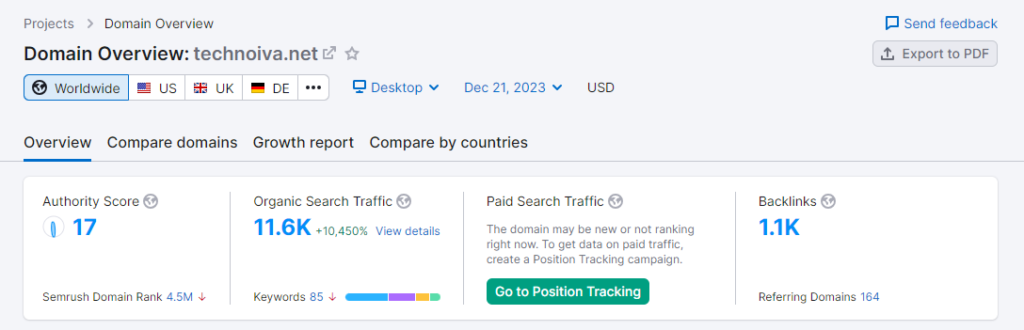
Ahref Traffic Stats
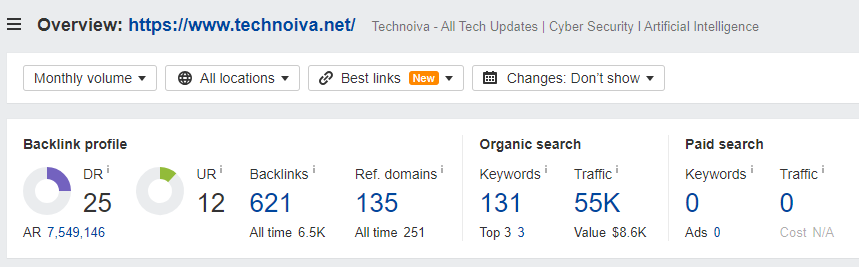
Submit A Guest Post On Any Of The Following Categories
Once you submit your post, give us time to review it. Our editors get so many requests, so we’ll publish your post when it’s reviewed.
- Technology Updates
- Internet
- Cyber Security
- Machine Learning
- Data Science
- Education
- Blockchain
- Big Data
- DevOps
- Digital Marketing
- Android & iOS Apps
- Ethical Hacking
- Virtual Reality
- Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT)
- Information Technology (IT)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Cloud Computing
- Computers
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
- Gadgets
- Mobile Apps
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Education
- How To Articles
- Business
- Study Abroad
How To Find Us
Tech Blog “guest article”
Tech Blog “this is a guest post by”
Tech Blog “contributing writer”
Tech Blog “want to write for”
Tech Blog “submit blog post”
Technology + “write for us” + guest post
Tech blogs write for us
Tech write for us
tech and marketing write for us
write for us study abroad
write for us study in usa
write for us masters in usa
write for us data science
write for us machine learning
fintech “write for us”
“Write for us” + tech blog
Tech + “guest post.”
“write for us” tech
Gadgets “Write for Us”
Tech “write for us”
Tech “guest article”
Tech “this is a guest post by”
Tech “contributing writer.”
Tech “want to write for”
Tech “submit blog post”
Tech “suggest a post”
Tech Blog “guest post”
Tech blogs + “write for us”
If you have any questions then please feel free to contact us
